Tanning Bed Tips: Achieve the Ultimate Indoor Tan
Many people love the look of sun-kissed, radiant skin, but outdoor tanning can be unpredictable because of weather, limited sunlight, and uneven exposure. Indoor tanning beds solve this problem by giving you full control over your tanning experience.A tanning bed is an enclosed device lined with fluorescent lamps that emit ultraviolet (UV) light. When your skin absorbs UV radiation, it triggers melanin production, darkening the skin. Modern tanning beds are designed to mimic sunlight with controlled UV levels for shorter, more consistent sessions. You can choose the session length, light intensity, and comfort level, making it possible to tan anytime during the year. With the right tanning bed tips, you can build a gradual, natural-looking glow without the risks that come from staying too long in direct sunlight. Understanding how tanning beds work, preparing your skin before each session, and following proper aftercare are key steps to achieving the best results. Whether you are a beginner or already familiar with indoor tanning, learning safe and effective methods helps you reach your ideal color while keeping your skin healthy, smooth, and evenly toned.
A Brief History of Indoor Tanning
The first tanning bed appeared in the 1970s in Germany. It was introduced to the United States soon after as “indoor sunshine.” Early models focused on high UVB output, which often led to burns. Over time, new designs improved safety and comfort, making tanning accessible year-round.
The Popularity and Purpose of Tanning Beds Today
Tanning beds remain popular among people who want fast, even results. They’re used for cosmetic reasons and sometimes for mood improvement during darker months. However, moderation is crucial. Many users follow professional tanning bed tips to maintain skin health and avoid overexposure.
How Tanning Beds Work
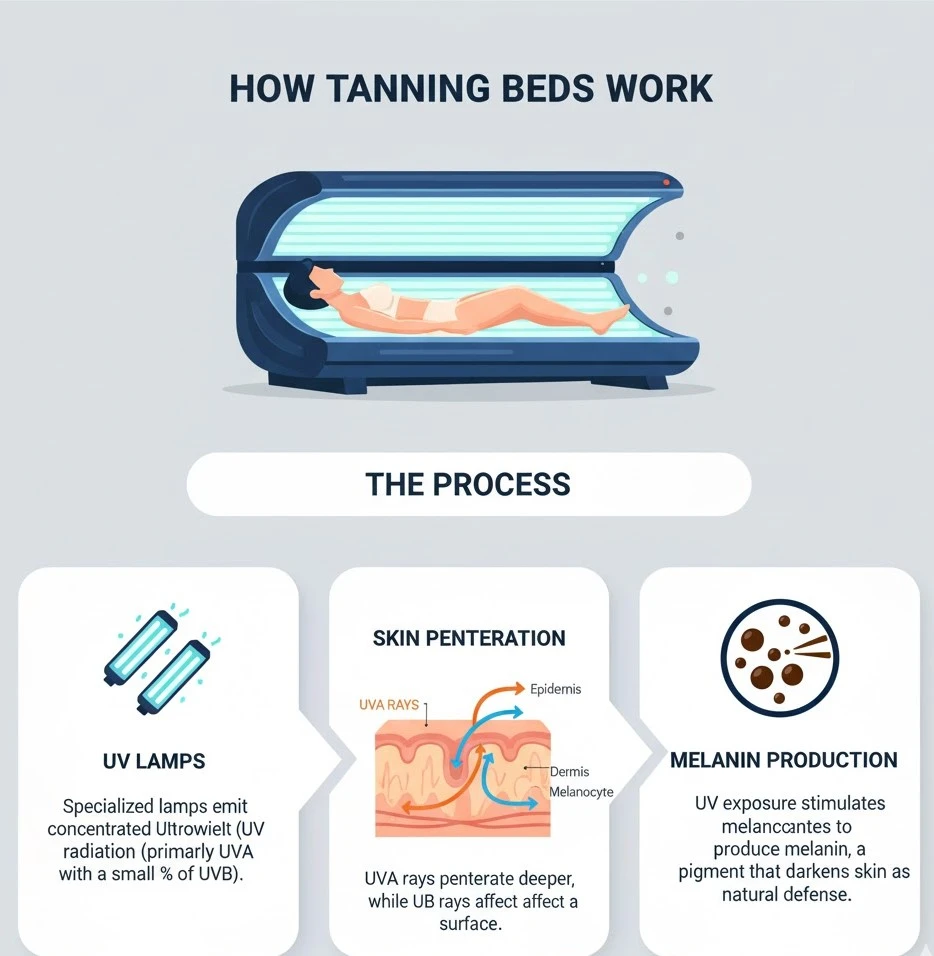
To tan effectively, you need to understand what happens inside the bed. UV light interacts with your skin to stimulate melanin and produce color. Knowing the science helps you tan smarter and protect your skin.
Understanding UV Light (UVA vs. UVB Rays)
Tanning beds emit both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays penetrate deeper, creating long-lasting color, while UVB rays trigger the initial pigment response. Most modern beds balance both for a natural tone.
| Type of Ray | Depth of Penetration | Main Effect on Skin |
|---|---|---|
| UVA | Deep (dermis) | Long-term pigmentation |
| UVB | Superficial (epidermis) | Stimulates melanin, can cause burns |
The Science Behind Skin Pigmentation and Melanin Production
When UV light reaches the skin, cells called melanocytes release melanin. This pigment acts as your skin’s defense system, absorbing UV light and reducing damage. The more melanin you have, the deeper your tan appears.
Types of Tanning Beds (Low-Pressure, High-Pressure, Hybrid)
Different beds produce different effects.
| Type | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Pressure | Emits both UVA and UVB | Natural gradual tan |
| High-Pressure | Mostly UVA light | Faster, longer-lasting color |
| Hybrid | Combines both | Balanced tone with lower burn risk |
Choosing the right bed depends on your skin type, tanning goals, and how often you plan to tan.
Preparing for a Tanning Bed Session
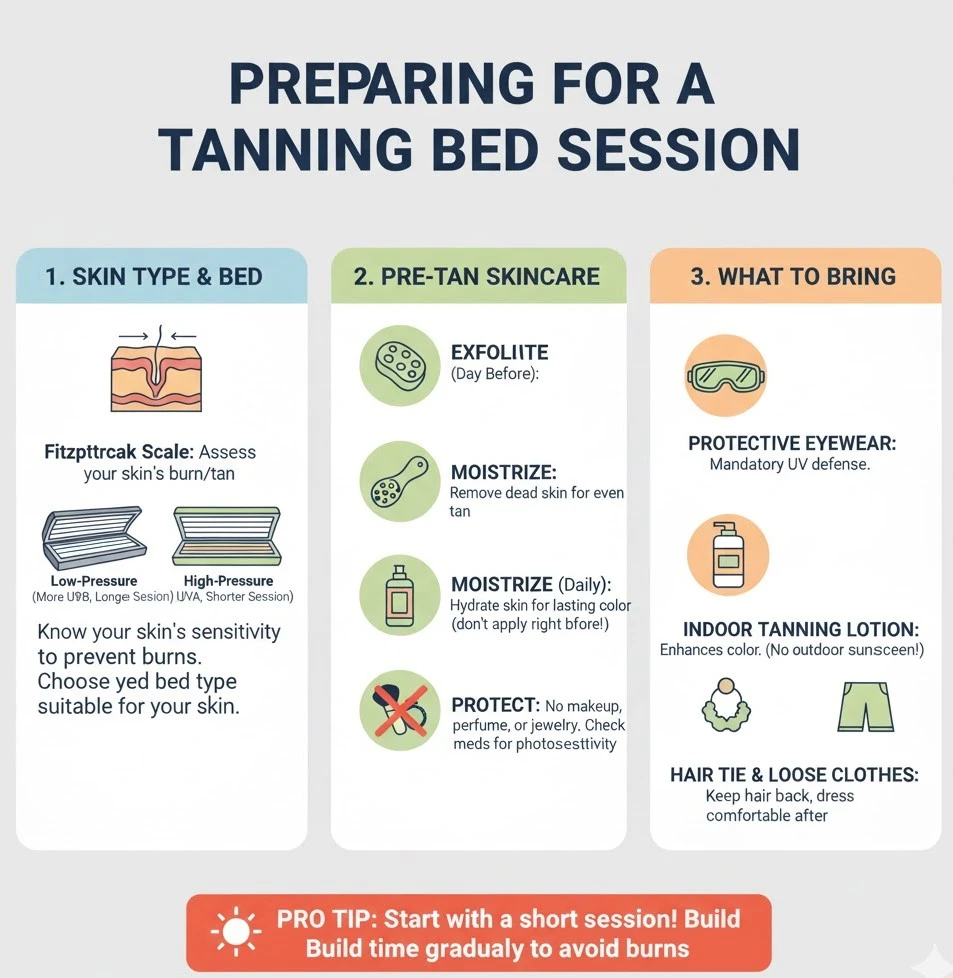
Preparation is key to a safe and even tan. Proper skin care before your session can make your results smoother, deeper, and longer lasting.
Skin Type Assessment and Choosing the Right Bed
Before you tan, identify your skin type using the Fitzpatrick scale (Types I–VI). Fair skin (Type I–II) burns quickly, so shorter sessions and gentle beds are safest. Medium to darker tones can tolerate more exposure but still need moderation.
Pre-Tan Skincare Routine (Exfoliation, Moisturizing, and Protection)
Exfoliate a day before your session to remove dead skin cells. Apply a light moisturizer a few hours prior to tanning to keep the skin hydrated. Avoid perfumes, deodorants, or heavy creams that can block light absorption.
What to Wear and Bring to Your First Session
You can wear a swimsuit or go without clothing for an even tan. Always use protective eyewear provided by the salon. Bring lip balm and a towel. Avoid makeup and jewelry to keep your skin clear and safe.
How to Use a Tanning Bed Safely
Safety is non-negotiable. Proper session timing and protective gear make the difference between a healthy glow and overexposure.
Recommended Session Durations by Skin Type
Beginners should start with short sessions and gradually increase time.
| Skin Type | Suggested Time (Minutes) | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| I–II (Fair) | 3–5 | 1–2 times per week |
| III–IV (Medium) | 6–9 | 2 times per week |
| V–VI (Dark) | 8–12 | 2–3 times per week |
Never exceed the time recommended by your salon technician.
Importance of Eye and Skin Protection
UV rays can cause serious eye injuries and premature aging. Always wear approved goggles. Use indoor tanning lotions that protect and nourish the skin instead of outdoor sunscreens, which can block UV light entirely.
Common Mistakes to Avoid During Tanning
Avoid multiple sessions in one day, skipping protective eyewear, or using outdoor tanning oils. Don’t ignore your skin’s signals; redness means overexposure. Smart tanning bed tips include keeping track of time and skin reactions.
Achieving the Perfect Tan
Getting the ultimate tan takes patience. The best color builds gradually with consistent care and proper hydration.

Understanding Tanning Levels and Gradual Build-Up
Tanning salons often classify sessions into levels 1–6, each offering different UV intensities. Starting at a lower level and progressing ensures your skin adapts without burning.
Using the Right Tanning Lotion or Accelerator
Choose products designed for indoor tanning. Accelerators help build a base tan quickly. Bronzers add instant color. Always read ingredient labels and test on a small patch first.
Tips for Even and Long-Lasting Color
Keep your skin moisturized daily. Rotate positions inside the bed for balanced exposure. Drink plenty of water. Apply tan extenders or after-tan moisturizers to maintain even tone.
Aftercare for Tanning Bed Sessions
Your skin continues developing color hours after tanning. Post-session care protects your tan and keeps your skin smooth.
Hydration and Skin Moisturizing Tips
Use fragrance-free moisturizers rich in aloe vera or hyaluronic acid. These ingredients restore hydration and minimize dryness.
How to Prevent Peeling and Uneven Fading
Avoid hot showers right after tanning. Gently exfoliate every few days to remove dead skin and maintain an even look. Keep your skin moisturized to slow fading.
When to Schedule Your Next Session
Most people wait 48 hours between sessions. Your skin needs rest to regenerate and darken naturally. Once you reach your ideal color, maintain it with one session every 7–10 days.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Tanning Beds
Indoor tanning has both cosmetic appeal and potential risks. Being aware of both helps you make informed decisions.
Benefits – Confidence, Vitamin D, and Even Skin Tone
Many users report improved confidence and mood after tanning. Controlled UV exposure may support vitamin D production when used responsibly. Tanning beds also allow even coverage that outdoor sunlight can’t guarantee.
Risks – UV Exposure and Skin Damage Concerns
Excessive UV exposure increases the risk of premature aging and skin cancer. Overuse can cause dryness, burns, and pigmentation issues. Always follow expert tanning bed tips and limit exposure.
Safe Alternatives to Traditional Tanning Beds
If you prefer avoiding UV exposure, try spray tans or self-tanning lotions. These deliver color without radiation.
| Method | UV Exposure | Lasts | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanning Bed | Yes | 7–10 days | Real melanin tan | UV risk |
| Spray Tan | No | 5–7 days | Fast, safe | May fade unevenly |
| Self-Tanner | No | 4–6 days | Budget-friendly | Needs skill to apply |
Comparing Tanning Beds vs. Spray Tanning
Choosing between UV and sunless tanning depends on your skin type and desired tone.
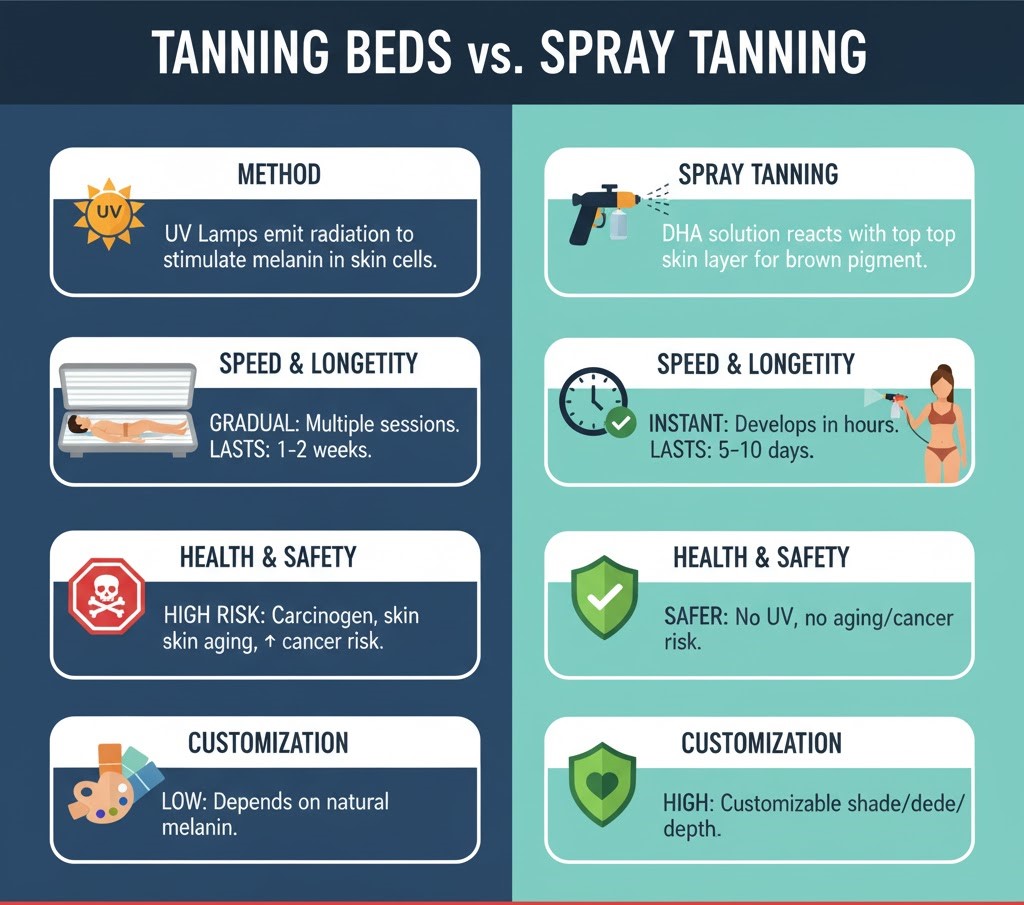
Key Differences in Process and Results
Tanning beds trigger melanin naturally through UV exposure, while spray tanning coats the skin with color compounds like DHA. Beds produce deeper tones, but spray tanning avoids UV risks.
Which Option Is Better for Your Skin Type?
If you have sensitive or fair skin, spray tanning is safer. Medium to darker tones can use tanning beds with moderation. Always test products on a small area before committing.
Combining Both Methods for a Balanced Glow
Some people combine both approaches. A base tan from UV sessions, followed by a spray tan, enhances depth and reduces total UV exposure. This hybrid approach balances color and safety.
| Feature | Tanning Beds | Spray Tanning |
|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Uses UV light to stimulate natural melanin production in the skin | Applies a fine mist of DHA (dihydroxyacetone) that reacts with the skin’s surface to create color |
| Result Type | Natural melanin-based tan that develops gradually | Cosmetic tan that appears instantly or within a few hours |
| UV Exposure | Yes, involves controlled UV rays | No UV exposure, completely sunless |
| Longevity | Usually lasts 7–10 days with proper care | Typically lasts 5–7 days depending on skincare routine |
| Ideal For | People seeking a deeper, long-lasting tan through gradual sessions | Those who want instant color or wish to avoid UV light |
| Maintenance | Requires regular sessions to maintain color | Needs reapplication as the tan fades from exfoliation |
| Skin Health | Must follow safe tanning bed tips to reduce UV-related risks | Safe for all skin types when applied correctly |
| Cost | Varies by salon and session level; often paid per session or package | Usually cheaper per session but may need more frequent visits |
| Customization | Can control session time and UV intensity for gradual build-up | Offers different shades and intensities for personalized tone |
| Comfort Level | Warm, relaxing experience similar to lying in the sun | Quick and cool mist process, often done in minutes |
Expert Tips and Myths About Tanning Beds
A lot of misinformation surrounds indoor tanning. Understanding the truth helps you make better choices.
Common Myths About Indoor Tanning (Debunked)
Myth 1: A base tan prevents sunburn. False. It provides minimal protection.
Myth 2: Tanning beds are safer than sunlight. They expose you to similar UV levels.
Myth 3: Darker skin doesn’t need protection. Every skin type can be damaged by UV light.
Dermatologists’ Tips for Safer Tanning
Experts recommend moderation, protective eyewear, and skin checks. Keep sessions brief and track your exposure history. Always apply a moisturizer after tanning to reduce dryness.
How Often Should You Tan Indoors?
Most professionals suggest one or two sessions per week for maintenance. Over-tanning leads to skin fatigue. Follow your salon’s schedule and reassess based on skin response.
Conclusion
Indoor tanning can be a convenient way to achieve a golden tone, but it requires care and discipline. Learn your skin type, follow proven tanning bed tips, and protect your eyes and skin every time. Healthy tanning is about balance, hydration, and consistency, not speed.
FAQs
1. How long should a beginner stay in a tanning bed?
Start with 3–5 minutes depending on your skin type. Gradually increase time as your skin adjusts.
2. Is tanning in a bed safer than tanning in the sun?
Both expose you to UV radiation. The bed offers control, but risks are similar if overused.
3. Can tanning beds help with vitamin D?
Yes, limited UVB exposure can stimulate vitamin D production, but sunlight or supplements are safer options.
4. What’s the best lotion for tanning beds?
Use indoor-specific accelerators or bronzers. Avoid outdoor oils and sunscreens.
5. How can I make my tan last longer?
Moisturize daily, drink water, and exfoliate lightly every few days. Avoid long hot baths and harsh soaps.